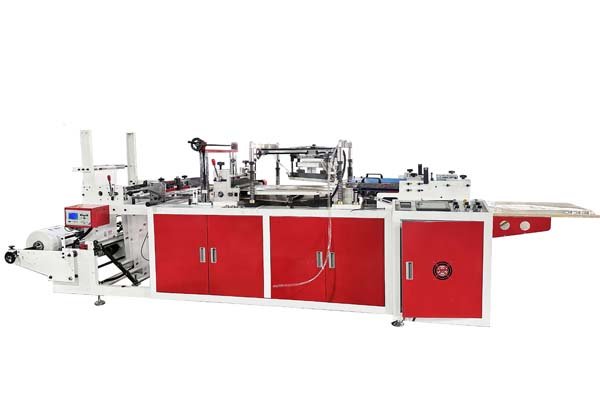
Ever wondered how those everyday plastic bags appear? It seems complex with all the different types out there. But, the basic process is quite straightforward once you break it down.
Plastic bags are made by melting plastic resin, extruding it into a thin film, sometimes printing on it, and then cutting and sealing the film into individual bags using specialized machines.
The journey from tiny plastic pellets to a finished bag involves several key stages. First, we select the right raw materials, usually polyethylene or polypropylene resins. These pellets are then melted down and pushed through a die in a process called extrusion. This creates a continuous tube or sheet of plastic film. This film is then cooled and can be printed with logos or designs if needed. Finally, our bag making machines1 take over to cut and seal the film into the desired bag shape and size.
We carefully control each step. For example, the extrusion temperature and cooling rate affect the film's strength and clarity. Printing requires precise alignment. And the cutting and sealing must be accurate to ensure every bag meets quality standards. It’s a mix of material science and precision engineering.
What raw materials are mainly used for plastic bags?
So, you know bags start as plastic, but what kind exactly? The specific material is super important for the final bag's properties.
The primary raw materials are polyethylene resins2, like Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) for flexible bags and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) for stronger, thinner bags. Polypropylene (PP) is also common for clearer, stiffer bags.

Common Plastic Resins
The choice of resin really depends on what the bag will be used for.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): This is probably what you think of for many shopping bags or food bags. It's flexible, pretty clear, and has good tear resistance. It’s great for bags that need to stretch a bit.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): This material is stronger and more rigid than LDPE, even when it's thinner. Think of grocery store produce bags or some types of t-shirt bags. It offers good moisture barrier properties.
- PP (Polypropylene): PP is known for its excellent clarity and higher stiffness. It's often used for packaging snacks, bread, or clothing because it makes the product look good. It also has a higher melting point, which can be useful.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Material | Common Uses | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| LDPE | Shopping bags, food storage bags, liners | Flexible, good tear resistance |
| HDPE | Grocery bags, trash bags, t-shirt bags | Strong, stiff, moisture barrier |
| PP | Food packaging (crisps, bread), retail bags | High clarity, stiffer, high melt point |
Additives and Their Roles
Besides the main resin, we sometimes add small amounts of other substances, called additives. These can change the plastic's properties.
- Slip agents: Make the bags feel smoother and easier to open.
- Anti-block agents: Stop layers of film from sticking together.
- Colorants: Give the bags various colors.
- UV stabilizers: Help protect the plastic if it's going to be exposed to sunlight for long periods.
At BagMec®, our machines are designed to work with a variety of these materials, including LDPE, HDPE, and PP films. We also work with customers using biodegradable options like PLA, adapting our machines to handle these newer, eco-friendlier materials.
What types of machines make plastic bags?
Making plastic bags isn't a one-machine job for the whole process. It starts with the film, then the bag itself.
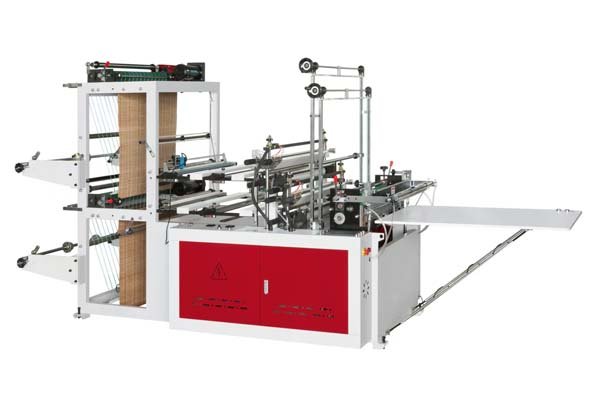
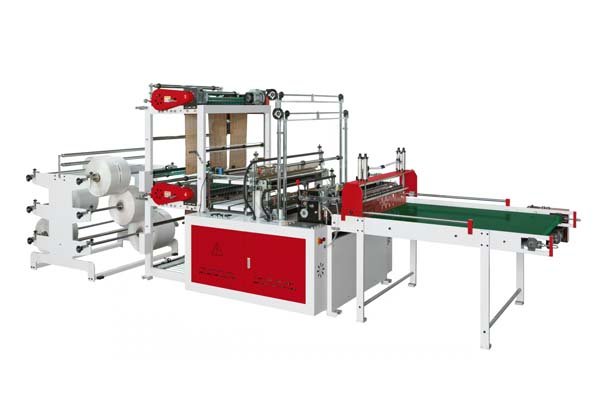
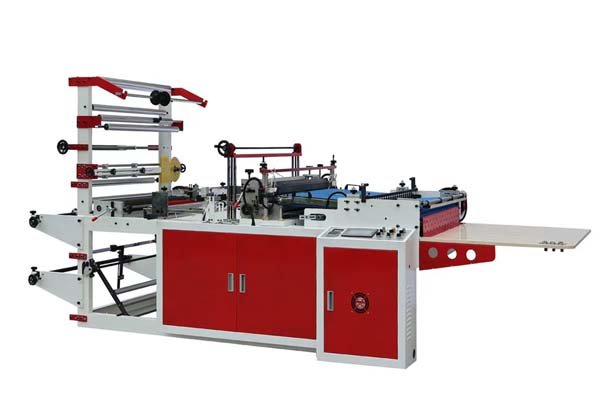
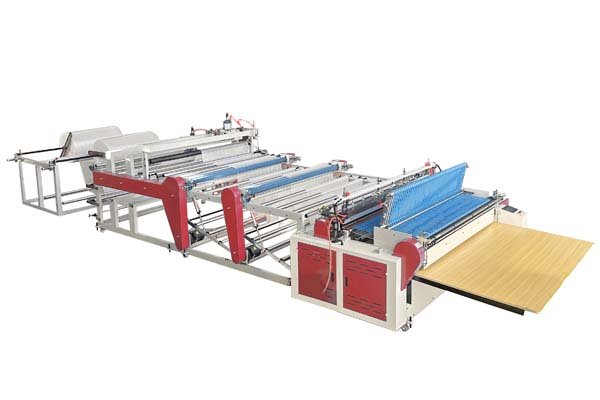
The main machines are film extruders3, which create the plastic film from resin, and bag making machines, which then cut, seal, and form the film into bags. Different bag styles require specific types of bag making machines.
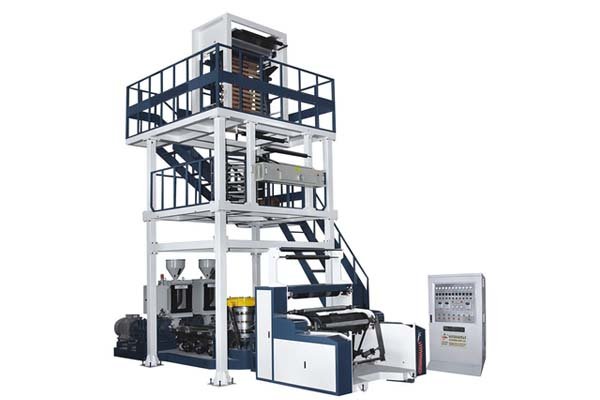

Film Extrusion Machines
First, you need the plastic film.
- Blown Film Extruders: These are very common. They melt plastic resin and extrude it upwards or downwards through a circular die, forming a continuous tube of film. Air is blown into the tube to expand it, like a long balloon. This process helps to orient the plastic molecules, which can make the film stronger. The tube is then cooled, flattened, and wound onto rolls.
- Cast Film Extruders: Here, melted plastic is extruded through a flat die onto a chilled roller. This process can produce very clear and consistent film, often used for lamination or high-quality packaging.
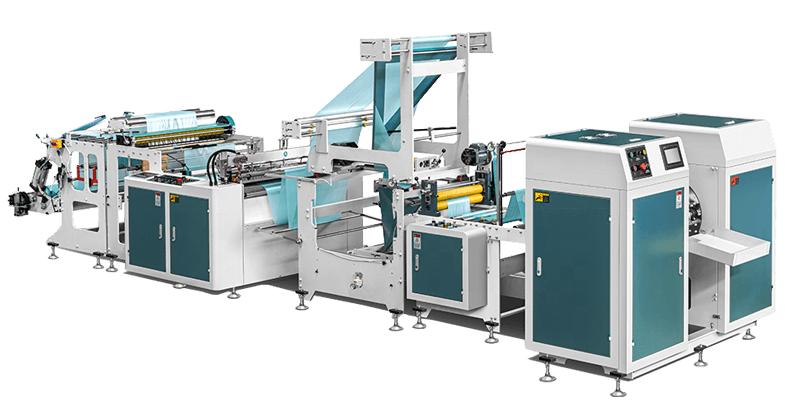
Core Bag Making Machines
Once we have rolls of plastic film, the bag making machine does the rest. The type of machine depends on the bag you want to make. At BagMec®, we manufacture a wide range:
- Side Seal Bag Machines: These machines take one or two layers of film and seal the sides. They are great for things like food packaging or general merchandise bags. Our Side Sealing Bag Machines generally range from $10,500.00 to $18,500.00.
- Bottom Seal Bag Machines: These machines make bags by sealing the bottom edge of a flattened tube of film. Garbage bags and produce bags are often made this way. Our Garbage Bag Machines, for example, are priced between $23,000.00 and $35,000.00.
- T-Shirt Bag Making Machines: These are specialized for making those familiar t-shirt style shopping bags with built-in handles. They involve cutting and sealing to create the handles and the bag body. Our T-Shirt Bag Making Machines cost from $17,000 to $32,000.
- Specialty Machines: There are many others too!
- Wicketer Bread Bag Machines ($69,000.00-$88,000.00): For bags used in automatic bread packaging lines.
- Courier Bag Machines ($23,000.00-$35,000.00): For durable mailer bags, often with adhesive strips.
- Zipper Bag Making Machines ($15,000.00-$22,000.00): To create reclosable bags.
- Patch Handle Bag Machines ($8,500.00-$15,500.00): For retail bags where a separate patch is heat-sealed to create a reinforced handle.
Each machine is designed for efficiency and precision for its specific bag type.
How does a bag making machine actually work?
You've got the film, you've got the machine. But what happens inside that machine?
A bag making machine unwinds the plastic film, feeds it through guides, uses a heated bar to seal layers together, and then a blade cuts the film to create individual bags. Many machines can also add features like handles or perforations.
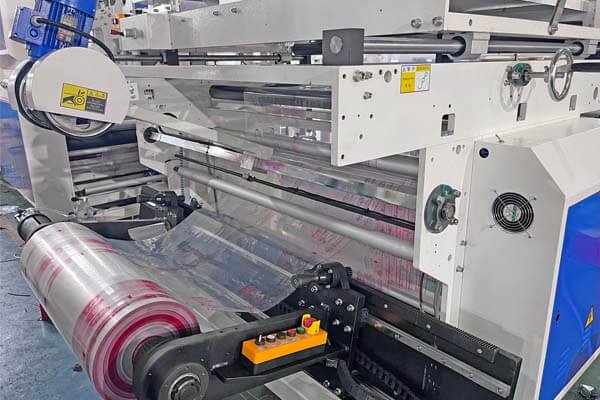

Key Operational Stages
- Film Unwinding and Feeding: The roll of plastic film is mounted on an unwinder. The film is then pulled into the machine. Consistent film feeding is vital. Our BagMec® machines often feature "Smart Tension Control" to ensure the film feeds smoothly without stretching or sagging.
- Printing or Accessory Application (if applicable): If the bag needs printing and it wasn't done on the film beforehand, some machines can do inline printing. Others might apply patches for handles or attach zippers at this stage.
- Sealing Process: This is where the bag shape starts to form.
- Heated sealing bars press against the film. The heat and pressure melt the plastic layers together, creating a seam.
- The type of seal depends on the bag:
- Bottom seal: A single bar seals across the bottom of a folded film or tube.
- Side seal: Bars seal the sides of folded film or two separate film layers.
- Star seal (for some garbage bags): A more complex seal that gathers the bottom of the bag.
- Cutting: After sealing, a blade cuts the film to separate one bag from the next. This could be a hot knife that also seals the edge as it cuts, or a cold knife.
- Stacking and Collection: Finished bags are then stacked or collected, ready for packing.
Automation and Control
Modern bag making machines, like those we build at BagMec®, are highly automated.
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): This is the brain of the machine. It controls the timing, temperature, speed, and all other operations. Operators use touchscreen interfaces to set parameters and monitor production.
- Servo Motors: We use energy-saving servo motors in many of our machines. These provide very precise control over movement (like film feeding and cutting), which improves bag quality and reduces energy consumption by up to 30%.
- Sensors: Various sensors monitor things like film position, temperature, and bag count to ensure everything runs correctly.
This automation helps us make bags very quickly and consistently. For example, some of our high-speed shopping bag machines can produce over 1,200 bags per hour!
Conclusion
Making plastic bags involves transforming raw resin into film, then precisely cutting and sealing that film using specialized machines. This process allows for a wide variety of bag types and customizations.
-
Discover the various types of bag making machines and their specific functions in the plastic bag manufacturing process. ↩
-
Explore this link to understand the significance of polyethylene resins in the production of plastic bags and their properties. ↩
-
Learn about the crucial role of film extruders in creating plastic films, essential for bag production. ↩