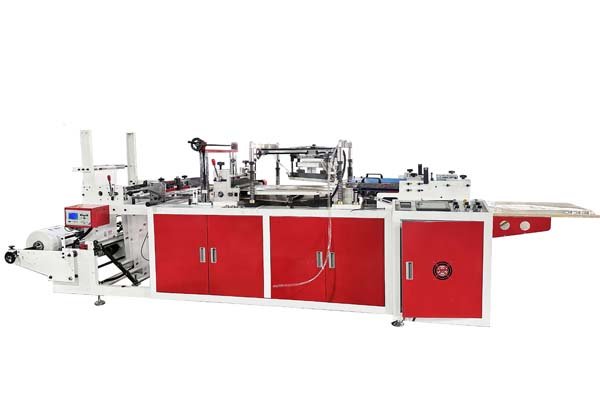
Wondering about the sheer volume of plastic bags1 in 1000 pounds? It's a common question, but the answer isn't straightforward. Many factors change the final count, which can be confusing.
The number of plastic bags in 1000 pounds can range from roughly 40,000 to over 90,000, and sometimes even more. This wide range depends heavily on the individual bag's type, thickness, and size.
This significant variation exists because plastic bags aren't all made the same. Think about the flimsy produce bag from the grocery store versus a sturdy retail shopping bag or a thick industrial sack. Each has a different weight. So, to figure out how many bags make up 1000 pounds, we first need to understand what kind of bag we're talking about. The material density and the amount of material used per bag are the primary drivers of this calculation.
The weight of a single bag is the most crucial factor. For example, lightweight T-shirt bags, common in many stores, weigh very little. This means you'd need a huge number of them to reach 1000 pounds. On the other hand, heavy-duty bags, like those used for construction debris or large-volume retail, are much thicker and larger, so fewer of them would make up the same weight.
What Factors Influence the Weight of a Single Plastic Bag?

So, you see the count isn't fixed. Several key characteristics of a plastic bag determine its individual weight. Understanding these helps clarify why the number of bags in 1000 pounds varies so much.
The primary factors influencing a single plastic bag's weight are its material composition2 (like LDPE or HDPE), its thickness (often measured in microns or mils), and its overall dimensions (length and width).
Unpacking Bag Weight Variables
Let's explore these factors in more detail. Each plays a vital role in the final weight of any given plastic bag. As manufacturers, we at BagMec® consider these every day.
Material Type – The Starting Point
The type of plastic resin used is fundamental.
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE): Often used for softer, more flexible bags like bread bags or dry-cleaning bags. It's less dense than HDPE.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): This is stronger and more rigid. Think of typical grocery store T-shirt bags or some retail bags. It can be made very thin yet retain strength.
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for its clarity and strength, often used for food packaging bags or clear retail display bags.
- Biodegradable/Compostable Materials (e.g., PLA blends): These materials have different densities and properties compared to traditional plastics, which will also affect weight.
The choice of material, which we expertly handle with our machines like Food Package Bag Machines or specialized PLA film machines, sets the base weight.
Thickness – The Substance of the Bag
Thickness, or gauge, is a major weight contributor. It's typically measured in:
- Mils: One mil is a thousandth of an inch.
- Microns (µm): One micron is a thousandth of a millimeter.
| Bag Application | Typical Thickness Range (Microns) | Typical Thickness Range (Mils) |
|---|---|---|
| Produce Bags | 8 - 15 µm | 0.3 - 0.6 mil |
| T-Shirt/Grocery Bags | 12 - 25 µm | 0.5 - 1.0 mil |
| Retail Shopping Bags | 40 - 75 µm | 1.5 - 3.0 mil |
| Heavy-Duty/Courier Bags | 60 - 150 µm | 2.4 - 6.0 mil |
Thicker bags use more material per unit, so they weigh more. Our Heavy Duty Bag Machines and Courier Bag Machines are designed to handle these thicker films effectively.
Size and Dimensions – The Area Covered
Naturally, a larger bag will use more material than a smaller one, assuming the same material and thickness. The length, width, and presence of any gussets (folds that allow the bag to expand) all add to the surface area, and thus, the material used. A small patch handle bag will weigh much less than a large garbage bag, even if made from the same film.
Additional Features – The Extras
Features beyond the basic bag body also add weight:
- Handles: Die-cut handles, patch handles, or loop handles (like those made by our Loop Handle Bag Making Machine) all add material.
- Zippers: Zipper closures, as seen on bags from our Zipper Bag Making Machine, add a strip of plastic.
- Printing: Ink adds a very small amount of weight, but for heavily printed bags, it can be a minor factor.
- Reinforcements: Extra layers or thicker sections, especially around handles or seals, increase weight.
How Does Bag Design Directly Impact the Number of Bags Per Pound?

Now we know what makes a bag heavy or light. This naturally leads to how design choices affect the count per pound. It’s about optimizing for purpose while being mindful of material usage.
Efficient bag design3 aims for the necessary strength and functionality with minimal material. Thicker films, larger sizes, or added features like handles mean fewer bags per pound, while streamlined designs increase that number.
Design Choices and Material Efficiency
When we design a bag or, more accurately, when our customers use our machines to produce bags, every design element has an implication for material consumption and thus, weight.
The Quest for Material Optimization
The goal for many manufacturers is to produce a bag that meets its functional requirements (carrying capacity, durability, barrier properties) using the least amount of material possible. This is not just for cost savings on raw materials but also for reducing shipping weight and environmental impact.
- Example: A T-Shirt Bag Making Machine is designed to produce thin, lightweight bags that are surprisingly strong due to their HDPE material and folded gusset design. This maximizes the number of bags per pound.
Balancing Strength and Weight
For applications requiring more robust bags, like heavy groceries, industrial parts, or courier shipments, a heavier design is unavoidable.
- Heavy Duty Bags: Our Heavy Duty Bag Machines produce bags from thicker films by design. These bags weigh more individually, so you get fewer per pound, but they offer superior puncture resistance and carrying capacity.
- Laminated Pouches: Machines like our Lamination Pouch Making Machine create multi-layer structures for enhanced barrier properties or print quality. These layers inherently add weight.
Here’s a hypothetical comparison to illustrate (weights are approximate and vary widely):
| Bag Type | Material Example | Est. Weight per Bag (grams) | Approx. Bags in 1000 lbs (453,592g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thin Produce Bag | LDPE film | 2g | ~226,796 |
| Standard T-Shirt Grocery Bag | HDPE film | 5g | ~90,718 |
| Boutique Retail Bag | LDPE/HDPE blend | 15g | ~30,239 |
| Heavy-Duty Courier Bag | Co-extruded PE | 30g | ~15,119 |
| Large Industrial Liner | LDPE/LLDPE | 70g | ~6,479 |
(Note: 1000 pounds is approximately 453,592 grams.)
The Role of Advanced Machinery
Modern bag making machines, like those we produce at BagMec®, offer features that help control material usage precisely.
- "Smart Tension Control": This patented technology ensures consistent film feeding, reducing variations in bag dimensions and therefore weight.
- Precision Cutting and Sealing: Accurate cutting and strong, neat seals (like from our Side Sealing Bag Machine) minimize waste and ensure each bag conforms to its design specifications.
- Automation: Fully automated systems help maintain consistency run after run, leading to more predictable bag weights.
Why Is Knowing the Bag Count Per Pound Important?

This might seem like a purely academic question. But knowing the bag count per pound has very real-world applications. It’s not just about curiosity; it’s about practical planning and efficiency.
Knowing the bag count per pound is crucial for logistics, accurate cost calculation, effective material procurement, and for assessing recycling volumes or environmental impact linked to material usage.
Practical Applications of Bag Weight Knowledge
Understanding this metric helps businesses and organizations in several key areas.
For Bag Manufacturers and Users
- Costing: When we price our machines, or when our customers price their bags, the amount of raw material (resin) is a primary cost driver. Knowing bags per pound helps in calculating resin consumption and per-unit cost.
- Quoting Projects: If a customer needs, say, one million courier bags, the manufacturer needs to calculate the total weight of plastic required, which directly impacts raw material orders and shipping costs for the finished goods.
- Logistics and Shipping: Weight and volume determine shipping costs. Fewer, heavier bags or more, lighter bags will pack and ship differently. This is vital for planning pallet loads and truck space. Our customers, like the Indian Logistics Giant using our courier bag machines, depend on this.
For Recycling Operations
Recycling centers often measure collected plastics by weight.
- Estimating Volume: Knowing an average bags-per-pound for different types of plastic helps them estimate the sheer number of items they are processing. For example, the Trout Lake Nature Center reported 41,000 bags in 1,000 lbs, likely of mixed post-consumer bags.
- Processing Capacity: This data helps in understanding the capacity of balers and other processing equipment.
For Environmental Reporting and Initiatives
Understanding material usage is key to sustainability.
- Life Cycle Assessment: Companies trying to reduce their environmental footprint need to know how much material goes into their packaging.
- Material Reduction Goals: If a company switches to a lighter bag design (perhaps enabled by a more advanced machine like those offering "Energy-saving servo motors"), they can quantify the material savings by comparing bags per pound. Our work with the US Eco-Brand on biodegradable PLA film machines is an example of this focus.
For Procurement and Inventory Management
Businesses that purchase large quantities of bags for their operations (e.g., retail chains, e-commerce fulfillment centers) use this information.
- Storage Space: Knowing how many bags are in a pound, and thus in a box or on a pallet, helps plan warehouse space.
- Ordering Cycles: It aids in determining how much to order and when to reorder to maintain adequate stock.
Conclusion: Understanding the Count
So, 1000 pounds of plastic bags can mean many different quantities. The key is knowing the bag's specific type, thickness, size, and material. This understanding is vital for business, logistics, and recycling efforts.
-
Understanding the types of plastic bags can help you grasp their weight variations and how they impact the count in 1000 pounds. ↩
-
Exploring material composition will clarify why different plastics lead to varying bag weights, crucial for understanding counts per pound. ↩
-
Learning about bag design practices can reveal how manufacturers optimize for strength and weight, impacting the number of bags per pound. ↩